Optimized Application Protocols for Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel
|
Application |
Description |
Example Cell Type / Model |
Key Features |
|
Coating culture plates with diluted Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel to improve cell attachment, spreading, and physiological morphology. |
Epithelial cells, endothelial cells, stem cells |
Promotes natural adhesion and maintains differentiation potential under physiological stiffness. |
|
|
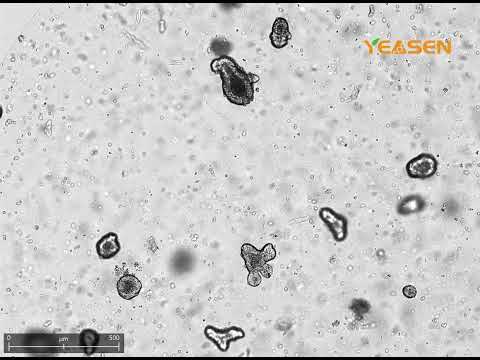
Embedding cells or organoid fragments within Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel to simulate native ECM conditions. |
Intestinal organoids, tumor spheroids, stem cell-derived organoids |
Enables self-organization, tissue polarity, and long-term culture stability. |
|
|
Forming a 3D matrix barrier using Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel to assess cell migration and invasion capabilities. |
Tumor cells (e.g., MDA-MB-231, A549) |
Reproduces ECM remodeling and invasive behavior under controlled gradients. |
|
|
Using Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel as a scaffold for endothelial tube formation and vascular network modeling. |
HUVECs, microvascular endothelial cells |
Supports rapid capillary-like tube formation and quantitative angiogenesis analysis. |
|
|
Mixing tumor cells with chilled Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel prior to subcutaneous or orthotopic injection in mice. |
Cancer cell lines, patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) |
Enhances cell viability, local retention, and tumor take rate in vivo. |
|
|
Employing Ceturegel™ Matrix Gel as an ECM-mimicking substrate to assess platelet adhesion and clot formation. |
Endothelial or platelet adhesion models |
Provides physiologically relevant matrix stiffness for coagulation and thrombosis research. |