|
Components |
Volume (μL) |
Volume (μL) |
Final Concentration |
|
2× Hieff UniconTM Universal TaqMan multiplex qPCR master mix |
10 |
12.5 |
1× |
|
Primer mix (10 μmol/L) |
x |
x |
0.1-0.5 μmol/L |
|
Probe mix (10 μmol/L) |
x |
x |
50-250 nmol/L |
|
Rox reference dye |
0.4 |
0.4 |
1× |
|
Template DNA/cDNA |
1-10 |
1-10 |
- |
|
ddH2O |
up to 20 |
up to 25 |
- |
Description
Hieff Unicon™ Universal Blue qPCR Master Mix (Probe Based) is a pre-solution for 2×real-time quantitative PCR amplification characterized by high sensitivity and specificity, is blue in color, and has the effect of sample addition
This product is a 2× Mix pre-mixed reagent that enables up to four fluorescent quantitative PCR reactions in a single reaction well. This product contains the genetically modified antibody method to hot-start Taq enzyme, greatly improving the amplification sensitivity and specificity. At the same time, this product has deeply optimized the multi-reaction buffer, which can improve the amplification efficiency of the reaction and promote the effective amplification of low-concentration templates. This product can be used for genotyping and multiplex quantitative analysis.
Features
- Strong tolerance of blood impurities
- High sensitivity
- Super storage stability
Applications
- Pathogen detection
- Copy number analysis
- SNP genotyping
Specifications
| Hot Start | Built-in hot start |
| Detection method | Primer-probe detection |
| PCR method | qPCR |
| Polymerase | Taq DNA polymerase |
| Type of sample | DNA |
| Application equipment | Applied Biosystems: 5700, 7000, 7300, 7700, 7900HT Fast, StepOne™, StepOne Plus™, 7500, 7500 Fast, ViiA™7, QuantStudio™ 3 and 5, QuantStudio™ 6,7,12k Flex; Bio-Rad: CFX96, CFX384, iCycler iQ, iQ5, MyiQ, MiniOpticon, Opticon, Opticon 2, Chromo4; Eppendorf: Mastercycler ep realplex, realplex 2 s; Qiagen: Corbett Rotor-Gene Q, Rotor-Gene 3000, Rotor-Gene 6000; Roche Applied Science: LightCycler 480, LightCycler 2.0; Lightcycler 96; Stratagene: MX3000P™, MX3005P™, MX4000P™; Thermo Scientific: PikoReal Cycler; Cepheid: SmartCycler; Illumina: Eco qPCR. |
Components
| No. | Name |
11211ES03 100T |
11211ES08 500T |
11211ES20 2,000T |
11211ES61 10,000T |
| 11211 |
Hieff Unicon™Universal Multiplex qPCR Master Mix (Probe Based) |
1 mL | 5×1 mL | 20 mL | 100 mL |
PCR Reaction setup
Rox reference dye is optional
Cycle Setup
| CYCLE STEP |
TEMPERATURE |
TIME | CYCLES |
| Initial Denaturation |
95°C | 5 mins |
1 |
| Denaturation Extension |
95°C 60°C |
15 secs 30 secs |
40-45 |
Shipping and Storage
The product is shipped with dry ice and can be stored at -15℃ ~ -25℃ for 2 year.
Figures
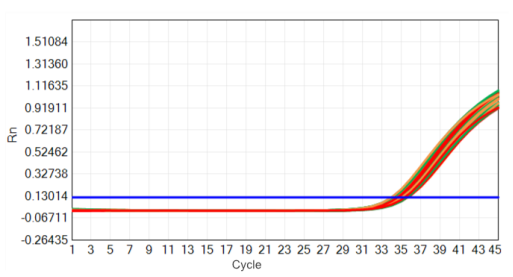
Figure 1 High stability: 37℃ thermal acceleration stability
The red line: 37℃ thermal acceleration 0 day; The yellow line: 37℃ thermal acceleration 7 days; The green line: 37℃ thermal acceleration 14 days
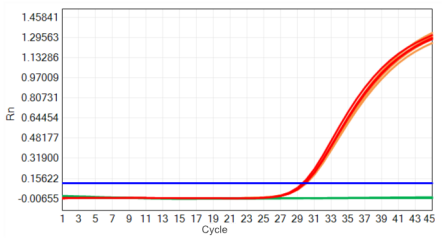
Figure 2 High stability: freeze-thaw stability
The red line: freeze thaw o time; The yellow line: freeze thaw 50 times; The green line: NTC
FAQ
Q: What is the amount of the template X? What is the commonly used amount?
A: (1) The amount of template DNA is something that the experimenter needs to figure out during the first experiment. First, dilute the template DNA (generally, a 5-10 fold dilution is recommended), then load the samples at different template concentrations, and select the optimal loading amount with a CT value ranging from 20 to 30.
(2) The commonly used amount is 500-1000 ng of total RNA for reverse transcription, which is diluted 10 times and 1 μL of cDNA is taken for the qPCR experiment. Q: What is the validity of the qPCR experiment results? Why is it recommended that the Ct value should be greater than 15?
A: a) The effectiveness must meet the following three conditions:
(1) Standard curve: Amplification efficiency range: 90 - 110%, corresponding slope is
-3 -- 3.5. R2 > 0.98. (Amplification efficiency = 10^(-1/slope - 1)), when the slope = -3.32, the amplification efficiency = 100%.
(2) Amplification curve: A S-shaped curve, with the Ct value ranging from 15 to 35. The Ct value of the negative control is greater than 35 or there is no Ct value. (3) Melting curve: A single peak.
b) The 10 times the standard deviation of the fluorescence values for 3 to 15 cycles is the fluorescence threshold. A too small Ct value will affect the curve.
Q: What is the function of Rox?
A: ROX is a reference dye. Its function is to standardize the non-PCR oscillations in the fluorescence quantitative reaction, correct the sample addition errors or the errors between wells, and provide a stable baseline.
Q: Why is the amplification curve unstable (with a jagged plateau in the amplification curve)?
A: Possible reasons:
a) The purity of RNA is low, and there are many impurities in the system; recommended parameters: OD260/OD280 = 1.8 - 2.0, OD260/OD230 > 2.0. As the qPCR reaction progresses, the factors hindering the reaction keep increasing. If the RNA purity is low and there are many impurities, it will further affect the algorithm of the instrument platform's plateau, resulting in a sawtooth pattern.
b) The instrument has not been calibrated for a long time. Failure to calibrate the instrument will cause errors in the algorithm and result in various abnormal outcomes.
Solution:
a) First, increase the dilution factor of the template and observe the optimization effect. If the effect is still not satisfactory, it is recommended to prepare new high-purity RNA and conduct the experiment again.
b) Regularly (typically once a year) conduct instrument calibration and maintenance.
Q: Why doesn't the amplification curve reach the plateau stage?
A: Possible reasons:
a) The template quantity is too low (with a CT value of around 35). The recommended CT value range is: 15 < CT < 30. Reason: If the CT value is too high (such as CT > 30), the reaction stops after just a few cycles during the exponential amplification phase, thus preventing the attainment of the plateau phase.
b) The number of cycles is too small (30 cycles); a too low number of cycles (e.g. 35) causes the reaction to stop after just a few cycles when entering the exponential amplification phase. As a result, the plateau phase cannot be reached.
c) The amplification efficiency of the reagents is low (with a small CT value, but unable to reach the plateau stage, and the curve appears to be "stuck").
Solution:
a) Increase the template quantity; refer to the optimization method in Q1.
b) Increase the number of cycles; Recommended cycle count: Generally 40. For low-abundance genes, it can be set to 45.
c) Determine the amplification efficiency by making a standard curve. If the efficiency is indeed too low, then replace the reagents.
(d) Increase the concentration of Mg2+ (this will enhance non-specific amplification)
Q: Why do two peaks appear, and why is the lower peak Tm before 80℃?
A: Possible reasons for the lower peak Tm being before 80℃: The presence of primer dimers (generally, after mRNA reverse transcription, the product is around 100-150bp, and the peak corresponding to the Tm value is 80-90℃. If primer dimers exist, the size of the primer dimers is only a few dozen bp, and the peak corresponding to the Tm value is between 70-80℃. Therefore, a peak will appear before 80℃ and another peak will appear after 80℃). Low template concentration or high primer concentration.
Solution:
a) Appropriately increase the annealing temperature; b) Increase the template amount and reduce the primer concentration; c) Re-design the primers.
Q: Why do two peaks appear, and both of the peak temperatures are below 80℃?
A: Possible reasons for both peaks appearing before 80℃: During the quantitative analysis of MicroRNA, there was a problem with primer dimer formation. After reverse transcription of MicroRNA, the product size was around 80-90bp, and the Tm value corresponding to the peak was 70-80℃. If there was a primer dimer present, its size would only be a few dozen bp, and the Tm value corresponding to the peak would also be in the range of 70-80℃. Therefore, two peaks would appear before 80℃.
Optimization method: Optimization can be achieved through methods such as increasing the annealing temperature, reducing the primer concentration, or redesigning the primers.
Q: Why do two peaks appear, and why are the Tm values of both peaks after 80℃?
A: Possible reasons:
The poor specificity of the primers leads to the amplification of non-specific products.
b) Cross-contamination.
c) GDNA contamination can be confirmed through NRC testing.
Solution:
(a) Perform Blast to check the specificity of the primers. If there are any discrepancies, redesign the primers.
b) Perform operations in the ultra-clean bench. Pay attention to replacing the tip head to prevent cross-contamination.
c) Confirmation is carried out using the NRC negative control. If necessary, the template needs to be re-prepared.
Q: Why is it a unimodal distribution, but the Tm value is before 80℃?
A: Possible cause: The amplification product is a complete primer dimer, which might be due to the absence of a template.
Note: If it is microRNA, the result is normal (when performing microRNA quantification, there are primer dimers. After reverse transcription of microRNA, the product is approximately 80-90bp, and the peak corresponds to a Tm value of 70-80℃. If there are primer dimers present, the size of the primer dimers is only a few dozen bp, and the peak corresponding Tm value is also between 70-80℃. Therefore, two peaks will appear before 80℃).
Solution:
Perform high-resolution agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the presence of the target band, in order to determine whether the template has been added. Optimization method: Prepare a new and error-free reaction system and conduct experiments again.
Q: Why is it a single peak, but the peak is not sharp?
A: Possible reasons:
There are non-specific amplifications of similar size.
Solution:
(a) If the temperature range does not exceed 7℃, it is considered a valid result (that is, if the Tm value range is less than 7℃, it can be regarded as the same product);
(b) Perform high-concentration agarose gel electrophoresis (for high resolution) to confirm whether there is only one band.
[1] Zhang P, Lu S, Liu Z, et al. Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Profiling Reveals the Effect of LED Light Quality on Fruit Ripening and Anthocyanin Accumulation in Cabernet Sauvignon Grape. Front Nutr. 2021;8:790697. Published 2021 Dec 14. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.790697(IF:6.576)
[2] Xu B, Zhang C, Jiang A, et al. Histone methyltransferase Dot1L recruits O-GlcNAc transferase to target chromatin sites to regulate histone O-GlcNAcylation. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(7):102115. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102115(IF:5.157)
Related blog:
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Inquiry
You may also like
FAQ
The product is for research purposes only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic use in humans or animals. Products and content are protected by patents, trademarks, and copyrights owned by Yeasen Biotechnology. Trademark symbols indicate the country of origin, not necessarily registration in all regions.
Certain applications may require additional third-party intellectual property rights.
Yeasen is dedicated to ethical science, believing our research should address critical questions while ensuring safety and ethical standards.

