Description
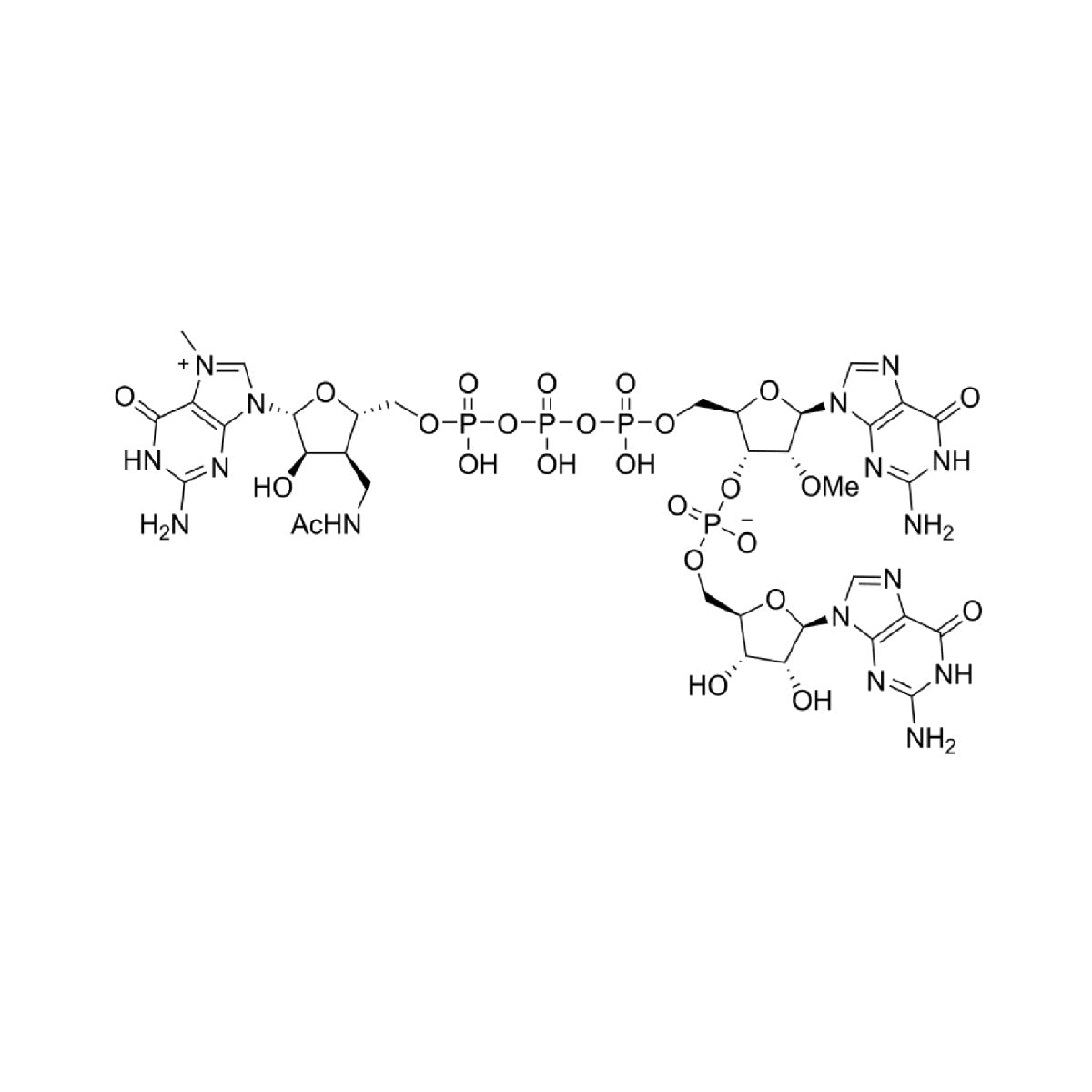
LZCap GG (3'Acm) is a cap1 analog. The product is used for transcription with the initial sequence of 5'GG3', and the natural cap1 structure is produced by Cap1 transcription capping.
US patent approved.
Components
|
Cat No. |
Name |
Size |
|
10686 |
LZCap GG (3'Acm) (50mM) |
100 μL |
|
1 mL |
Product Details
|
Molecular Formula |
C35H48N16O25P4 (Free acid) |
|
Molecular weight |
1216.19 (Free acid) |
|
Concentration |
50± 3 mM |
|
Purity |
HPLC ≥95% |
LZCap DNA Template Design
LZCap GG(3'Acm) is suitable for GG-initiated sequences. As shown in the figure below, the SP6 promoter (underlined) followed by the GG sequence can effectively initiate transcription.

Protocol
1. Thaw components required for the experiment on ice.
2. Add RNase free water and NTPs to reaction tube.
3. Heat LZCap GG(3'Acm) aliquot for 15 min at 60°C. Cool at room temperature for 5 min.
4. Immediately add LZCap GG(3'Acm) to tube and vortex to mix. Spin briefly to collect liquid.
5. Add 10x Transcription Buffer and vortex.
6. Add DNA template and SP6 Enzyme Mix.
7. Mix the prepared reaction solution, spin briefly, and incubate at 37°C for 2-3 hours. If the transcript length is less than 100nt, increase the reaction time to 4-8 h.
|
Component |
Volume (μL) |
Final concentration |
|
RNase Free Water |
Up to 20μL |
/ |
|
ATP(100mM) |
1 |
5mM |
|
UTP(100mM) |
1 |
5mM |
|
CTP(100mM) |
1 |
5mM |
|
GTP(100mM) |
0.2 |
1mM |
|
LZCap GG(3'Acm) (50mM) |
1.6 |
4mM |
|
10×Transcription Buffer |
2 |
1 × |
|
Linear DNA |
1μg |
50 ng/μL |
|
SP6 Enzyme Mix |
2 |
/ |
|
Final Volume |
20μL |
|
Notes:
1) The SP6 enzyme mix we recommended to used is MEGAscript® Kit(AM1330).
2) LZCap GG(3'Acm) is suitable for SP6 promoter transcription vector with 5 ‘GG 3’initiated sequences, which needs to be considered when constructing the vector.
3) The reagents, consumables and containers used in the experiment are free of RNase contamination.
4) It is recommended to use a linearized DNA template for transcription.
5) When modified nucleotides were used in place of wild-type nucleotides, the final concentration of the reaction was unchanged.
6) Modified N1-Me-pUTP can be used in place of wild-type UTP. The modified N1-Me-pUTP reduces the immunogenicity of mRNA. Henovcom can also provide modified nucleotide N1-Me-pUTP (Cat. No.: HN1002).
7) If the PCR product is used as the transcription initiation DNA template, the amount of DNA template can be reduced by half.
Storage
This product could be stored at -25~-15 ℃ for two years.
Precautions
- For your safety and health, please wear personal protective equipment (PPE), such as laboratory coats and disposable gloves, when operating with this product.
- For research use only.
F&Q
1. How do you design the LZCap?
Enzymes have a relatively "specific" recognition of substrates. Therefore, when designing a new cap structure, on one hand, we need novel structural modifications for patent purposes, but on the other hand, we strive to maintain similarity with natural/known structures as much as possible. The natural structure has a ribose 3' OH, which can be modified (e.g., methylation). Based on this consideration, we chose to add a carbon at the 3' position for patent novelty, followed by an NH to mimic the hydrogen bonding of OH, and then an acetyl group to reduce the basicity of NH and enhance its hydrogen bonding capability. The activity of LzCap is better than methylated natural cap, possibly due to increased hydrogen bonding. Compared to the methyl and methoxy groups, the acetyl amino group may also increase van der Waals interactions between the substrate (cap) and the initiating factor (enzyme).
2. Is the acetyl amino group stable?
The acetyl amino group is already sufficiently stable. It is much more stable than the 7-methylated position and the phosphodiester bond, which are the least stable parts of the cap.
Please contact us for more details about the LZCap licensing.
Payment & Security
Your payment information is processed securely. We do not store credit card details nor have access to your credit card information.
Inquiry
You may also like
FAQ
The product is for research purposes only and is not intended for therapeutic or diagnostic use in humans or animals. Products and content are protected by patents, trademarks, and copyrights owned by Yeasen Biotechnology. Trademark symbols indicate the country of origin, not necessarily registration in all regions.
Certain applications may require additional third-party intellectual property rights.
Yeasen is dedicated to ethical science, believing our research should address critical questions while ensuring safety and ethical standards.