Murine RNase Inhibitor-Avoiding RNase contamination
RNase contamination is always a concern when performing experiments involving RNA. Even with the cleanest of techniques, RNase contamination can happen and may have profound effects on data from downstream applications. High-quality, intact RNA is crucial to the success of sensitive applications. So, are there reagents that prevent RNA from being degraded? Yeah, murine RNase inhibitor of Yeasen is the best choice for solving this problem.
1. How to prevent RNA from being degraded?
2. What are RNase inhibitors?
3. What does RNase Inhibitor do?
4. What are the features of a Murine RNase Inhibitor?
5. Related products and performance
6. Related products
7. Frequently Asked Questions
1. How to prevent RNA from being degraded?
RNase plays an important role in nucleic acid metabolism and can be found in almost any type of prokaryote and eukaryote. RNase is secreted in body fluids such as tears, saliva, and sweat to defend against the invasion of microorganisms, and RNase is also present in skin debris. However, the main source of RNase in most environments is microorganisms, namely bacteria, and fungi. RNase is exceedingly hard to inactivate and exhibits high stability, heat resistance, acid resistance, and alkali resistance. After thermal denaturation, it can quickly regain its original structure. RNase is usually very active and is broadly distributed in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells and tissues. The RNA in the sample can completely degrade with just a trace amount of RNase contamination. RNase contamination in studies can come from both internal and external sources. RNase in cells is primarily an endogenous source of contamination, while exogenous sources include experimental supplies, the lab environment, and the experimenters themselves. RNases, especially members of the RNase A family, are small, compact proteins containing a few cysteine residues capable of forming many intramolecular disulfide bonds. After returning to room temperature, in the absence of a denaturing agent, the denatured RNase will restore its natural structure and some functions. Therefore, RNases retain considerable activity after repeated freeze-thaw cycles, even after autoclaving. The stable nature of these enzymes makes them resistant to many decontamination methods, which usually require aggressive chemical methods to eliminate RNases from surfaces and solutions.
To avoid the degradation of vulnerable RNA, Special precautions must be taken when working with RNA. To control exogenous RNase, the operator needs to wear gloves during the experiment, and change gloves after touching the skin, door handles, and the surface of ordinary objects. And the operator needs to use a special pipette gun for RNA operation, and use RNase-free wall tips, centrifuge tubes, compounds, and reagents. Keep away from or cover ventilation holes and open windows, and use less-traveled areas as RNase-free areas. And during RNA extraction and analysis, do not perform other experiments that may cause RNase contamination.
The method of inhibiting the activity of endogenous RNase is firstly to preserve the sample. After the tissue is sampled, the RNA should not be extracted directly. Instead, it should be quickly frozen and stored in a -80°C environment with liquid nitrogen in time, and the experiment should be carried out as soon as possible to minimize the degradation of RNA. RNase inhibitors are added to the cell lysate to simultaneously break cells and inactivate RNase, minimizing the activity of RNase released during cell breakage. All reagents and equipment must be specially treated to inactivate RNases before use.
In addition, RNA inhibitors can be used to inhibit RNase activity and prevent RNase degradation of RNA. There are several types of RNA inhibitors:
- Diethyl pyrocarbonate (DEPC): It is a strong but not complete RNase inhibitor. It denatures the protein through the combination of the imidazole ring of histidine in the active gene group of RNase, thereby inhibiting the activity of the enzyme.
- Guanidine isothiocyanate: Currently considered to be the most effective RNase inhibitor, it can also inactivate RNase while lysing tissue, which can destroy cell structure and dissociate nucleic acid from nucleoprotein, and also has a certain effect on RNase Strong denaturing effect.
- Vanadyl ribonucleoside complex: a complex formed by vanadium oxide ions and nucleosides, which can combine with RNase to form a transitional analog, almost completely inhibiting the activity of RNase.
- Protein inhibitor of RNase (RNasin): an acidic glycoprotein extracted from rat liver or human blastodisc, RNasin is a non-competitive inhibitor of RNase, which can bind to a variety of RNases, making it Inactivate.
- Others: SDS, urea, diatomaceous earth, etc. also have a certain inhibitory effect on RNase.
2. What are RNase inhibitors?
RNase inhibitors are a class of substances that can inhibit RNase activity. Common RNase inhibitors include Diethyl Pyrocarbonate (DEPC), Guanidine Isothiocyanate, Ribonucleoside Vanadyl Complexes (RVC), and protein inhibitors of RNase (RNasin). Among them, DEPC and guanidine isothiocyanate has certain toxicity, and the RVC has an inhibitory effect on PCR polymerase, which is not conducive to subsequent experiments. RNasin is not toxic and is a non-competitive inhibitor of RNase, which can bind to various RNases to inactivate them.
3. What does RNase Inhibitor do?
RNase inhibitors are commonly used as a precautionary measure in enzymatic manipulations of RNA to inhibit and control for such contaminants. RNasin is an acidic glycoprotein extracted from rat liver or human blastoderm, which can specifically bind to RNase in a non-covalent manner to form a complex, causing RNase inactivation, thereby protecting the integrity of RNA. At present, the RNase Inhibitor helps to prevent RNA degradation in applications like cDNA synthesis, RT-PCR, in vitro transcription/ translation reactions, or RNA purification.
4. What are the features of a Murine RNase Inhibitor?
Recombinant murine RNase inhibitors do not contain 2 oxidation-sensitive cysteines which are contained in human-origin RNase inhibitors. Therefore, murine RNase inhibitor has high anti-oxidation activity and is more stable for low DTT experiments. In addition, Murine RNase Inhibitor of Yeasen has the following features:
1) All-around RNase inhibition: Murine RNase Inhibitor of YEASEN specifically inhibits RNase A, RNase B, RNase C, and so on.
2) Versatile reaction conditions: RNase inhibitor is active at pH 5.0-9.0 and 25℃-55℃, which is suitable for thermostable reverse transcriptase.
3) Multiple downstream experiments possible: No inhibition of polymerase activity is observed when RNase Inhibitor is used with Taq DNA Polymerase, AMV or M-MuLV Reverse Transcriptase, or Phage RNA Polymerases (SP6, T7, or T3).
4) Mass-produced goods: a single manufacturing capacity of 2 billion U is helpful to cost management by ensuring product homogeneity, supply stability, and timeliness.
5) Batch-to-batch consistency: mature protein expression and purification platform by ISO13485 quality management system, quality control testing by quality requirements to assure product stability between batches.
5. Related products and performance
A. RNase Inhibitor blocks RNase activity
1μg HEK cell total RNA, 1μL RNase inhibitor can effectively inhibit 5ng RNase.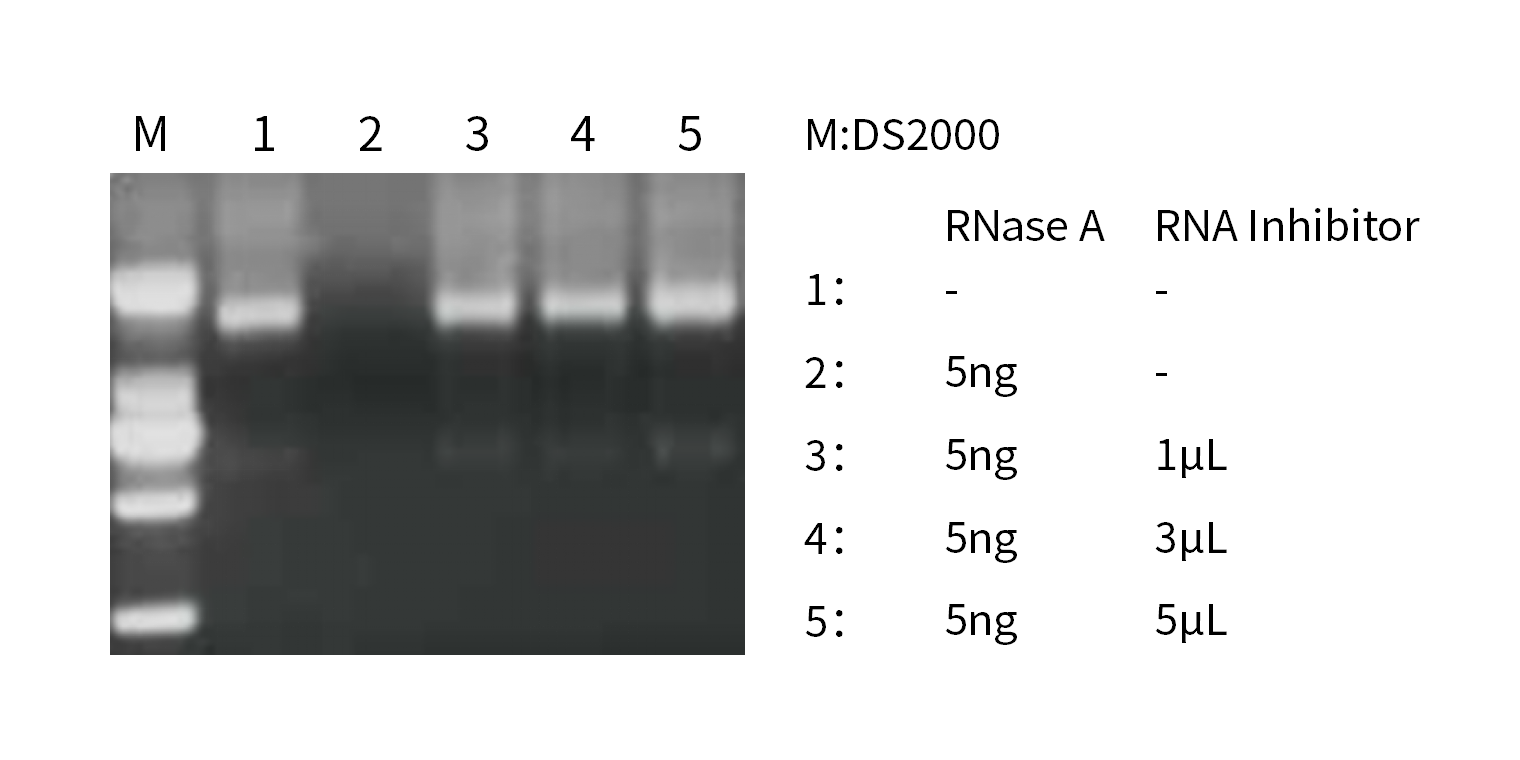
Figure 1. Inhibitory effect of Murine RNase Inhibitor.
B. RNase Inhibitor surpasses foreign products in qPCR testing
The inhibitory impact of the Yeasen and R* Company mouse-derived RNase inhibitors (MRI) was measured using the qPCR technique under identical experimental circumstances, and the RNase inhibitor of the YEASEN Murine source efficiently inhibited RNase A in the system. The impact of inhibition was superior to that of competitors.
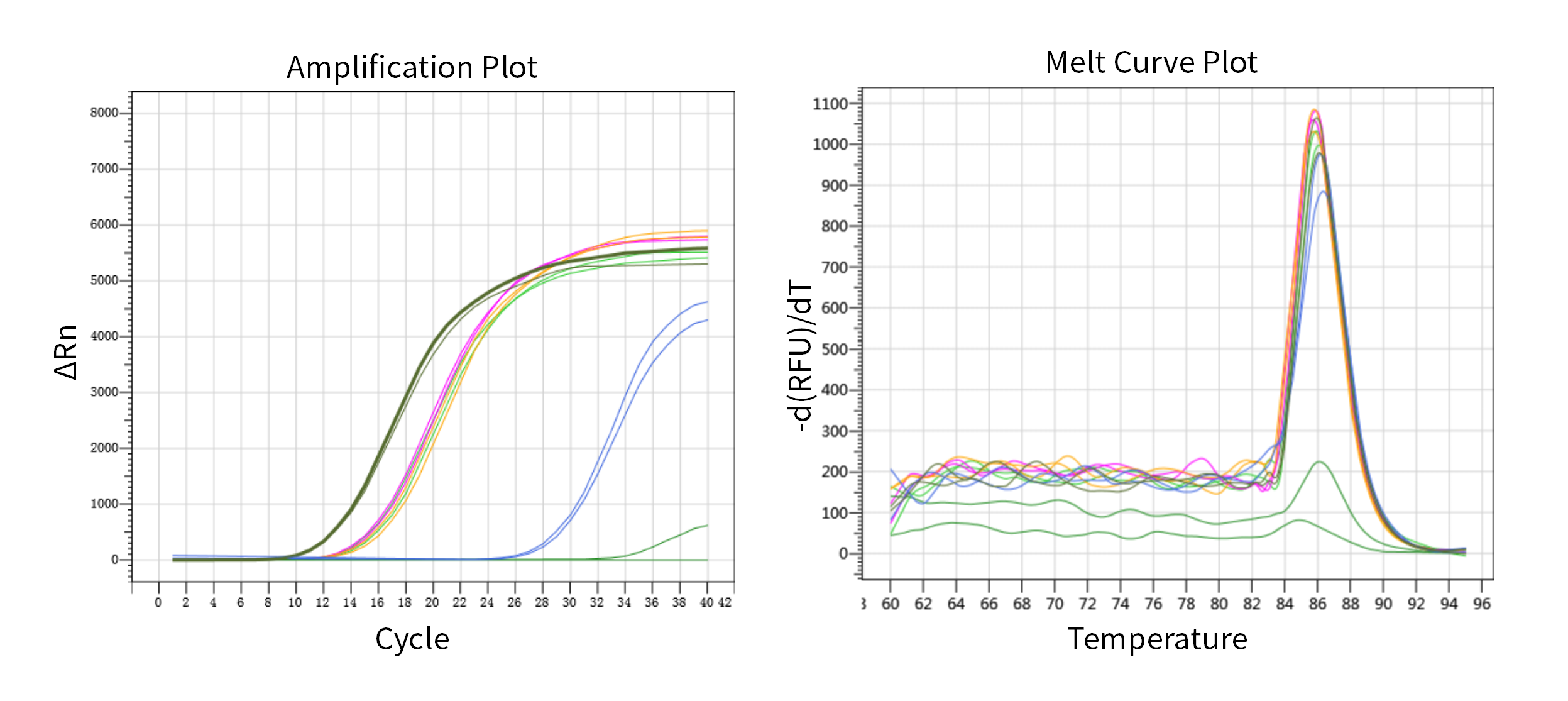
Figure 2. R* MRI RNase inhibition test
Note: The curves in the figure from left to right are: Positive control (RNA only, no RNase and MRI), 40 U MRI, 30 U MRI, 20 U MRI, 10 U MRI, and Negative control (RNA + RNase, no MRI).
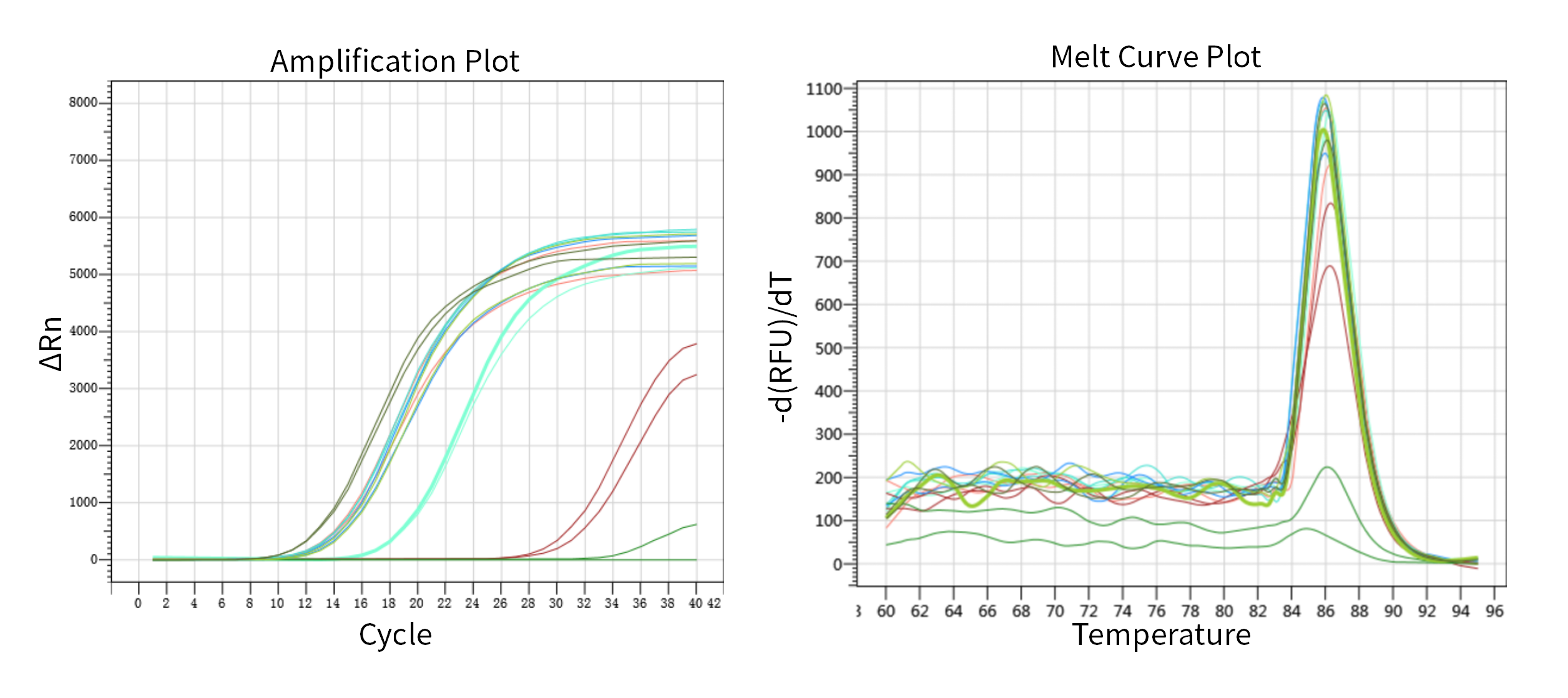
Figure 3. Yeasen MRI RNase inhibition test
Note: The curves in the figure from left to right are: Positive control (RNA only, no RNase and MRI), 80 U MRI, 60 U MRI, 40 U MRI, 30 U MRI, 20 U MRI, 10 U MRI, Negative control (RNA+RNase, no MRI).
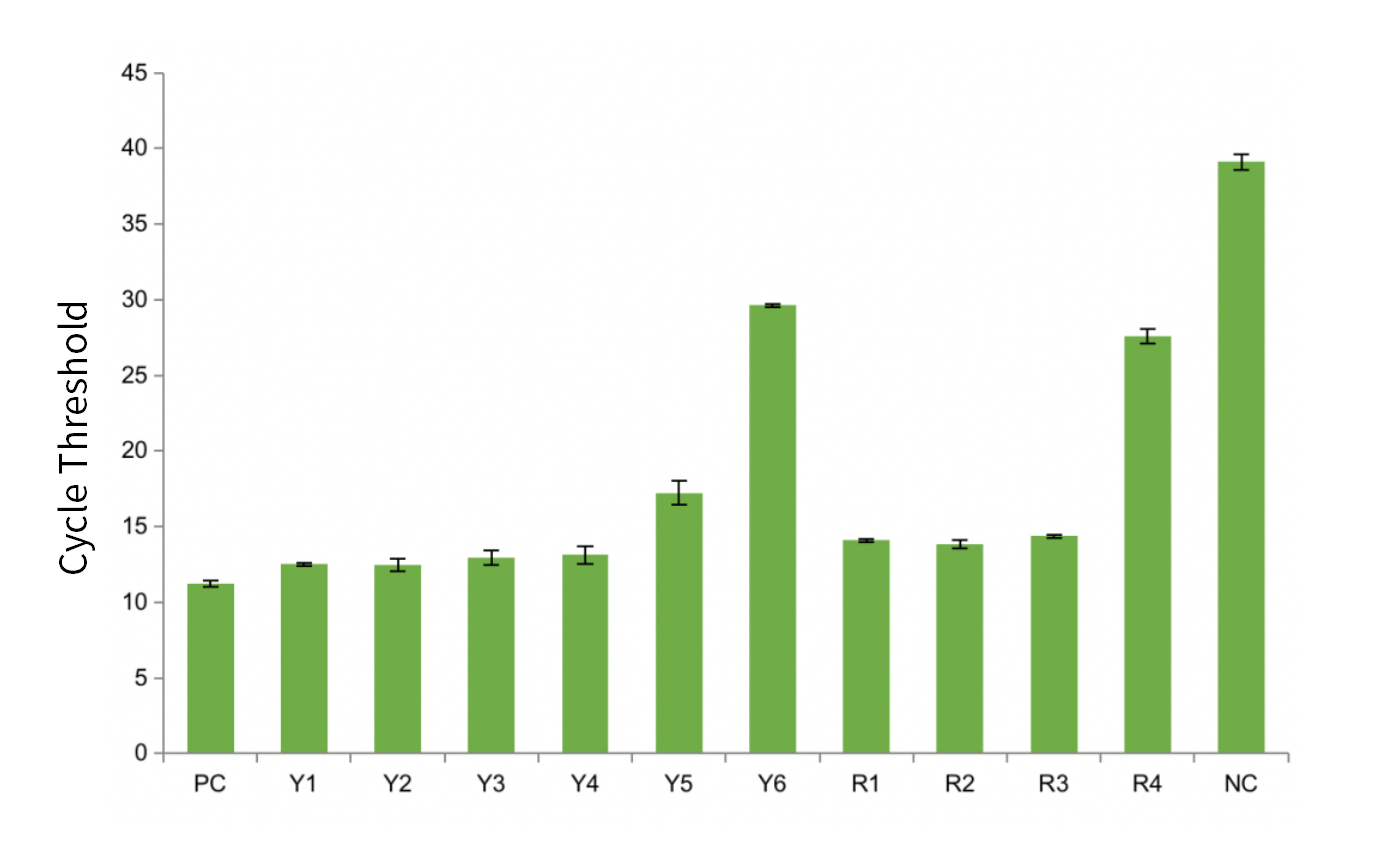
Figure 4. The CT of RT-qPCR results of Yeasen MRI and R* MRI
6. Related products
The related products that Yeasen can provide are shown in Table 1:
Table 1. List of Products
|
Product Name |
SKU |
Specifications |
|
10603ES05 |
2 KU |
|
|
10603ES10 |
10 KU |
|
|
10603ES20 |
20 KU |
|
|
10603ES60 |
100 KU |
|
|
10603ES94 |
20,000 KU |
|
|
Murine RNase inhibitor (200 U/μL) (Inquire) |
10610ES03 |
1 mL |
|
10610ES50 |
50 mL |
|
|
10610ES76 |
500 mL |
|
|
10703ES05 |
2 KU |
|
|
10703ES10 |
10 KU |
|
|
10703ES60 |
100 KU |
|
|
10703ES70 |
200 KU |
|
|
10703ES80 |
1,000 KU |
7. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: Will there be RNase in the Murine RNase inhibitor?
A: Each reagent will detect RNase activity to ensure that the Murine RNase inhibitor does not bring RNase contamination.
Q2: Will Murine RNase inhibitors have an impact on downstream PCR experiments?
A: It will have no effect. Each batch of Murine RNase inhibitor is clear of genomic contamination after quality testing and may be used in RT-PCR and RT-qPCR research.
Q3: Will the Murine RNase inhibitor be inactivated?
A: Inhibitors will be inactivated at temperatures above 65°C, and vigorous stirring will also cause inactivation.
Q4: What precautions should be taken when using a Murine RNase inhibitor to prepare the reaction system?
Answer: When preparing the system, an RNase inhibitor can be added first before other components that may introduce RNase contamination sources are added.
Q5: Does Murine RNase inhibitor have endonuclease and exonuclease activity?
Answer: There is no endonuclease and exonuclease activity, which helps to improve the product yield.
Regarding reading:
Murine RNase Inhibitors ——Successfully eliminate RNase contamination and preserve RNA
Reverse Transcriptase Selection
YEASEN Heat-labile UDG——Easily control aerosol pollution
High-quality isothermal amplification raw materials -Making RT-LAMP more sensitive and faster!
